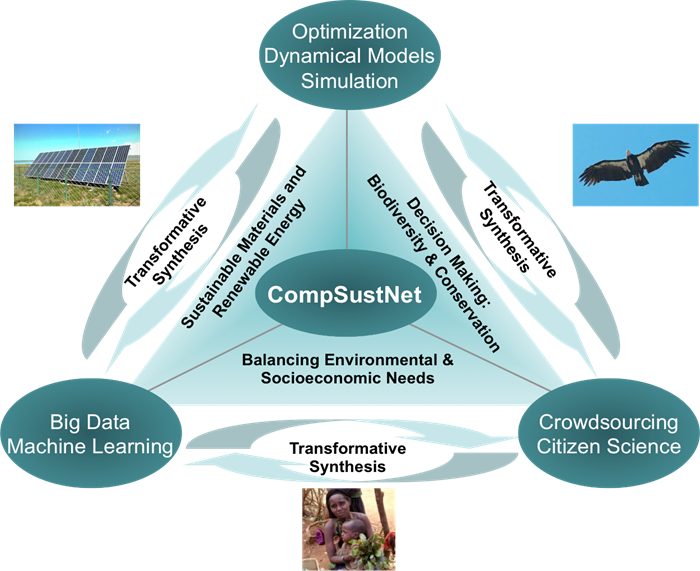
CompSustNet is a research network sponsored by the National Science Foundation through an Expeditions in Computing award. Thirteen U.S. academic institutions led by Cornell University, along with many national and international collaborators, are exploring new research directions in computational sustainability.
Interdisciplinary, multi-investigator research teams are focusing on cross-cutting computational topics such as optimization, dynamical models, big data, machine learning, and citizen science. These methods are being applied to sustainability challenges including conservation, poverty mitigation and renewable energy.
CompSustNet builds on the work of the Institute for Computational Sustainability (ICS), which started the field through one of the first NSF Expeditions awards in 2008. The virtual research lab includes educational, community building, and outreach activities to ensure that computational sustainability becomes a self-sustaining discipline.
Sample Projects
More sample project links
Photo: John Gregoire (JCAP/Caltech)
What: Rapid characterization of crystal structures from high-throughput X-ray diffraction experiments.
Why: Identify new materials for fuel cells, energy storage, and solar fuel generation.
How: Pattern decomposition, constraint and probabilistic reasoning, crowdsourcing.

Photo: DOE
What: Power grid modeling, control, and energy storage.
Why: Managing the power system with increasing use of renewable sources of electricity.
How: Stochastic optimization, sequential decision making, pattern decomposition.

Photo: Frank Annor (TAHMO)
What: Deploy 20,000 low-cost weather stations across Africa.
Why: Improve weather predictions, which is directly related food security.
How: Optimal placement, bayesian networks, multi-scale probabilistic modeling.

Photo: Santiago Molina
What: Socio-ecological corridor in the Ecuadorian Andes.
Why: Protect endangered Andean bear and other species in a significant biodiversity hotspot, while improving livelihoods of local communities.
How: Spatial capture-recapture, stochastic optimization, spatio-temporal modeling.

Photo: USC Teamcore
What: Protection Assistant for Wildlife Security (PAWS).
Why: Provide randomized patrol routes to combat poaching activity and protect wildlife.
How: Game theory-based analysis, spatio-temporal analysis, human behavior modeling, optimization.

Photo: Hong Liu (OSU)
What: Planning Algorithms for Resource Constrained Experimental Design.
Why: Efficiently identify biological and physical characteristics that maximize energy production from wastewater treatment.
How: Bayesian response surface modeling, budgeted optimization, simulation matching.
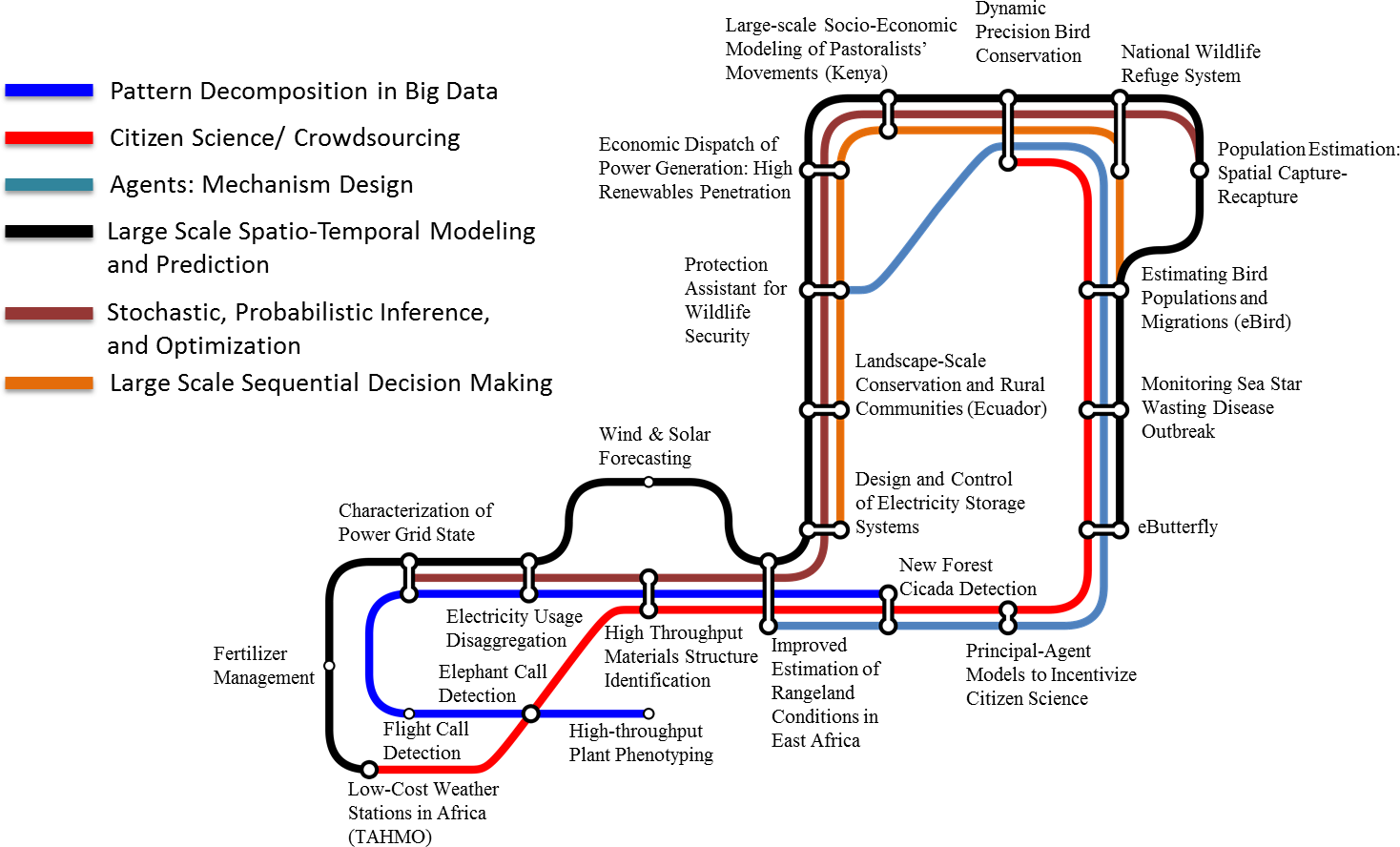
Examples of cross-cutting computational themes and projects